read: 704 time:2022-10-31 11:29:40 from:
Melt index is a value representing the fluidity of plastic materials during processing. It is based on the method of DuPont to identify the characteristics of plastics, and is also called melt flow rate.
Polypropylene is a thermoplastic resin obtained through propylene polymerization, which is mainly divided into isotactic polypropylene, random polypropylene and syndiotactic polypropylene. Strictly control the melt index of polypropylene to make the melt index within the corresponding allowable range, which is conducive to ensuring the good processability and quality of polypropylene products.
Melt Index Basic Overview
Melt index, MI, also known as melt flow rate, refers to the weight of polymer melt passing through the standard die within ten minutes under a certain temperature and load. The temperature is generally 230 ℃, the load is 2160g, and the standard die is 2.095mm. The higher the melt index, the better the fluidity of the polymer melt, and the lower the average molecular weight.
The main operation process of the test is as follows: First, place the polymer raw material to be tested, namely, plastic, in a small tank, and connect the end of the tank with a thin tube with a diameter of 2.095mm and a length of 8mm. Then, after heating to 230 degrees, extrude downward, and calculate the weight of the raw material extruded within ten minutes, which is the flow index of the plastic.
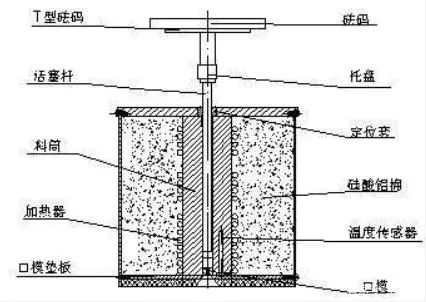
Study on Factors Influencing Melt Index of Polypropylene
一、 Factors Influencing Melt Index of Polypropylene
1. Explore the influence of hydrogen on the melt index of polypropylene
Under the action of Ziegler Natta, propylene polymerizes, leading to chain termination and chain transfer in the active center of polypropylene. On the basis of ideal chain termination and chain transfer, the catalyst activity is not destroyed, and the polymerization characteristics of the original catalyst system are not changed. There are two common cases of chain termination: one is that chain termination occurs under the action of chain terminators. Water, sulfur, arsenic and other related substances that can cause catalyst deactivation will lead to chain termination. Second β- H transfer: In the process of chain transfer, the active center transfers monomers in the direction of alkyl aluminum and olefins. In this process, it is necessary to add appropriate hydrogen as the chain transfer agent to control the molecular weight.
2. Melt index of polypropylene is affected by hydrogenation method
Hydrogenation methods mainly include parallel hydrogenation and distributed hydrogenation.
Parallel hydrogenation: hydrogen can be uniformly dispersed in the polymerization kettle, and the diffusion effect is good, so that the molecular weight in the reactor is very close, and the distribution rate is narrow. At the same time, the parallel hydrogenation method is difficult to accurately grasp the amount of hydrogenation.
Distributed hydrogenation: It is easy to operate and the process is simple. It only needs to add appropriate amount of hydrogen into the reactor. However, hydrogen addition to the last two reactors by slurry entrainment is easy to affect the amount of hydrogen addition and hydrogen diffusion effect.
The analysis of practice results shows that there is no difference between parallel hydrogenation and distributed hydrogenation in the product of melt index, but the main difference is the width of molecular weight distribution.
3 Effect of hydrogen diffusion on melt index of polypropylene
In this process, hydrogen diffusion and hydrogenation reaction are realized by stirring and gas circulation. The faster the stirring speed is, the better the hydrogen diffusion effect is. However, in actual conditions, hydrogen dispersion is generally improved through gas circulation within the allowable range of the process. When entering the kettle, the circulating gas continuously moves up from the bottom of the cauldron in the form of bubbles, thus increasing the contact surface between hydrogen and liquid propylene, increasing the uniformity of diffusion, promoting chain transfer reaction, increasing the heat removal effect, benefiting the production of polypropylene products with high melt index, reducing the fluctuation frequency of the melt index, and achieving the purpose of improving the melt index.
二、 Study on the Influence of Raw Materials on the Melt Index of Polypropylene
In this process, propylene is used as polymerization monomer, hydrogen is used as chain transfer agent, and appropriate Ziegler Natta is added as catalyst to help realize polymerization. The basic components of raw propylene include propylene purity, oxygen, carbon monoxide, arsenic, total sulfur, alkanes, water, carbon dioxide, etc. Among them, carbon monoxide, sulfur, arsenic, oxygen, water, unsaturated olefins, and water and oxygen in hydrogen may cause the deactivation of the active center of the catalyst.
In particular, although the high efficiency catalyst contains TiCl4 with a low occupancy, it has a serious impact on the trace impurities in the reaction medium and is easy to lead to poisoning. If the catalyst is deactivated due to serious poisoning, it will be difficult for the polymerization products to reach the specified melt index. In addition, there is a certain amount of inert gas in propylene. Although it will not affect the catalyst activity, if the content exceeds a certain range, it will occupy a large amount of reaction space, reduce the hydrogen partial pressure in the kettle, and make it difficult to control the melt index. It can be seen that purified hydrogen and refined propylene are helpful to maintain a stable melt index.
3、 Study on the Effect of Catalyst on Melt Index of Polypropylene
Under the same amount of hydrogenation, different catalysts lead to different melt indexes of products. Strictly speaking, the hydrogen regulation sensitivity is different due to the way of catalyst preparation and the different components in the catalyst. Therefore, if the catalyst needs to be replaced in the production process, the hydrogenation amount must be adjusted to keep its melt index within a stable range.
When the melt index of the production product is low, the difference between the melt index of the first reaction kettle product and the hydrogenation amount is not large. However, when the melt index of the production product is high, the difference between the melt index of the first reaction kettle product and the hydrogenation amount is large. Therefore, in the production of products, different hydrogenation amounts should be selected according to the specific conditions of the products, and the catalyst should be used reasonably.

Jincheng Petrochemical's 300000 ton polypropylene plant successfully trial production, 2024 polypropylene market analysis

The ABS market remains sluggish, what is the future direction?

Market differentiation of bisphenol A intensifies: prices rise in East China, while prices generally decline in other regions

The production method and process flow of silicone acrylic lotion, and what are the common raw materials