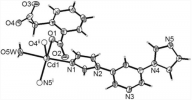
Calcium Carbide
Calcium carbide (CaC2) has a garlic-like odor and reacts with water to form acetylene gas plus calcium hydroxide and heat. In the past, it was used in miners’ lamps to continuously produce a small acetylene flame to provide some illumination in coal mines. Calcium carbide is used as a desulfurizer, dehydrant of steel, fuel in steel making, powerful deoxidizer and as a source of acetylene gas. It is used as a starting material for the preparation of calcium cyanamide, ethylene, chloroprene rubber, acetic acid, dicyandiamide and cyanide acetate. It is used in carbide lamps, toy cannons such as the big-bang cannon and bamboo cannon. It is associated with calcium phosphide and used in floating, self-igniting naval signalCalcium carbide is the most relevant carbide industrially because of its important role as the basis of acetylene industry. In locations where there is shortage of petroleum, Calcium Carbide is used as the starting material for the production of acetylene (1 kg of carbide yields ~300 liters acetylene), which, in turn, can be used as a building block for a range of organic chemicals (e.g. vinyl acetate, acetaldehyde and acetic acid). In some locations, acetylene is also used to produce vinyl chloride, the raw material for the production of PVC. A less important use of Calcium Carbide is related to the ferilizers industry. It reacts with nitrogen to form calcium cyanamide, which is the starting material for the production of cyanamide (CH2N2). Cyanamide is a common agricultural product used to stimulate early foliation. Calcium Carbide can also be employed as desulfurizing agent for producing low-sulfur carbon steel. Also, it is used as a reducing agent to produce metals from their salts, e.g., for direct reduction of copper sulfide to metallic copper. flares. Further, it is involved in the reduction of copper sulfide to metallic copper.